Comparing Value Systems
The Power of Vector Analysis in Ethical Debates
When comparing different value systems, it is useful to quantify their alignment or divergence explicitly. One rigorous and intuitive measure borrowed from vector mathematics is cosine similarity, which quantifies the angle between two vectors. Each value system can be represented as a high-dimensional vector, with each dimension corresponding to a specific ethical principle or value, assigned a weight based on importance.
How Cosine Similarity Works
Given two value vectors A⃗ and B⃗, cosine similarity is computed as follows:
Value of +1: Perfect alignment (vectors point exactly the same direction).
Value of 0: Orthogonality (values are entirely unrelated).
Value of -1: Direct opposition (completely contradictory).
Example: Christianity vs. Phosphorism
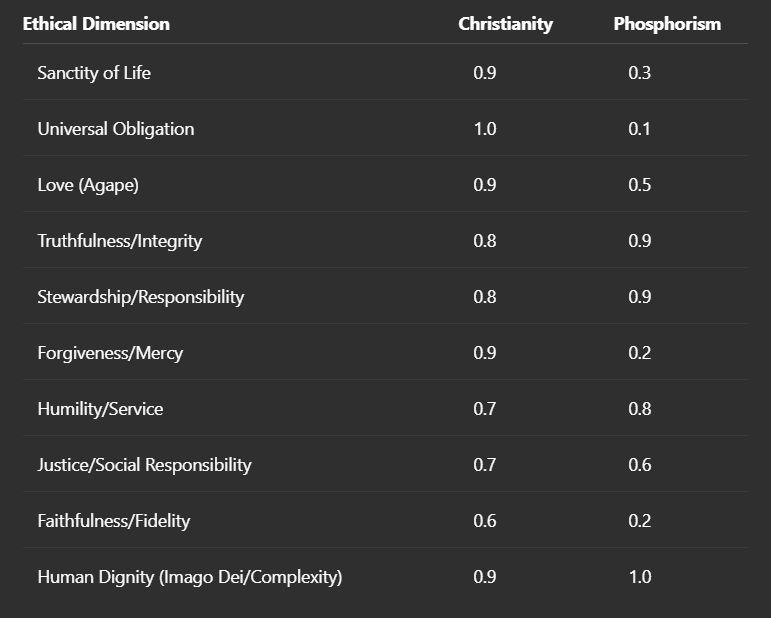
To illustrate this measure, we compare two value systems: Christianity and Phosphorism, each represented as 10-dimensional vectors, where each dimension corresponds to a central ethical value:
Computed Result
The cosine similarity between these two vectors was computed precisely as 0.842, indicating significant alignment. Despite differences—particularly on dimensions like "Universal Obligation," "Sanctity of Life," and "Forgiveness/Mercy"—the high similarity underscores considerable coherence, notably in values such as truthfulness, stewardship, humility, and respect for human dignity.
Interpretation and Applications
A cosine similarity of ~0.842 implies that Christianity and Phosphorism, though philosophically distinct, are more aligned than divergent. Such quantification helps clarify the practical potential for coexistence, collaboration, or necessary negotiation. It provides a clear method to anticipate sources of friction and alignment when integrating or comparing complex value systems in ethical debates, diplomacy, organizational alignment, and philosophical discourse.
Thus, the cosine similarity measure is not only mathematically elegant but practically insightful, offering a clear, quantifiable way to evaluate the complex interplay between diverse value frameworks.